Ever watched a bowling match and found yourself pondering whether that heavy ball knocking down pins is hollow or solid? Well, you’re not alone, trust us, the answer might just bowl you over.

Contents
Are All Bowling Balls Hollow
No, not all bowling balls are hollow. Most of them are, in fact, solid to the core!
A typical bowling ball is made up of a dense, heavy core surrounded by a lighter outer shell. This gives the ball its hefty weight and helps it hurtle down the lane to smash those pins.
So, What’s Inside the Bowling Ball?
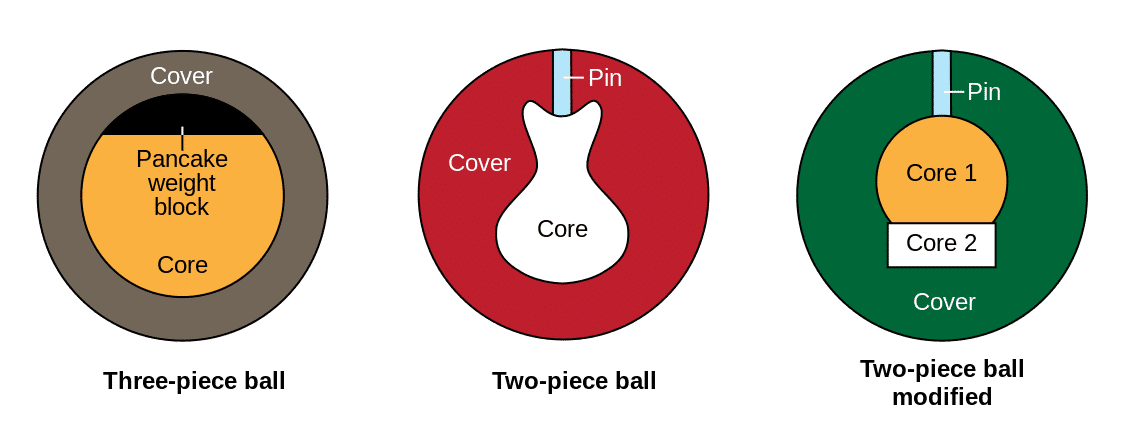
The Outer Shell or Coverstock
The outer shell, or coverstock, is usually made from plastic, urethane, reactive resin, or particle (proactive) materials. This layer interacts directly with the lane surface and plays a key role in the ball’s hook potential and reaction to the lane conditions.
The Filler
Between the core and the coverstock, there’s a layer of filler material. This filler is usually composed of lightweight plastic or similar materials. It’s meant to bring the ball up to its final weight without significantly altering the desired weight distribution achieved by the core and the coverstock.
The Core
The core of a bowling ball, often made from dense materials like resin or ceramic, is designed to be heavy. This is where the majority of the ball’s weight comes from. The shape of the core also contributes to the ball’s overall balance and spin. Here are a few cores commonly found in bowling balls:
Pancake Core
The pancake core is the simplest and most common form of a bowling ball’s core. Named for its flat, disc-like shape, this core type is typically found in entry-level and beginner balls. It gives the ball a stable, predictable roll, perfect for new bowlers getting familiar with the game.

The Pancake Core of the Bowling Ball
Symmetrical Core
Symmetrical cores, as the name suggests, have an even, balanced shape. This shape allows for a smooth rolling motion and consistent hook potential, regardless of how the ball is drilled. These cores are often found in bowling balls used by intermediate and advanced players.

The Symmetrical Core
Asymmetrical Core
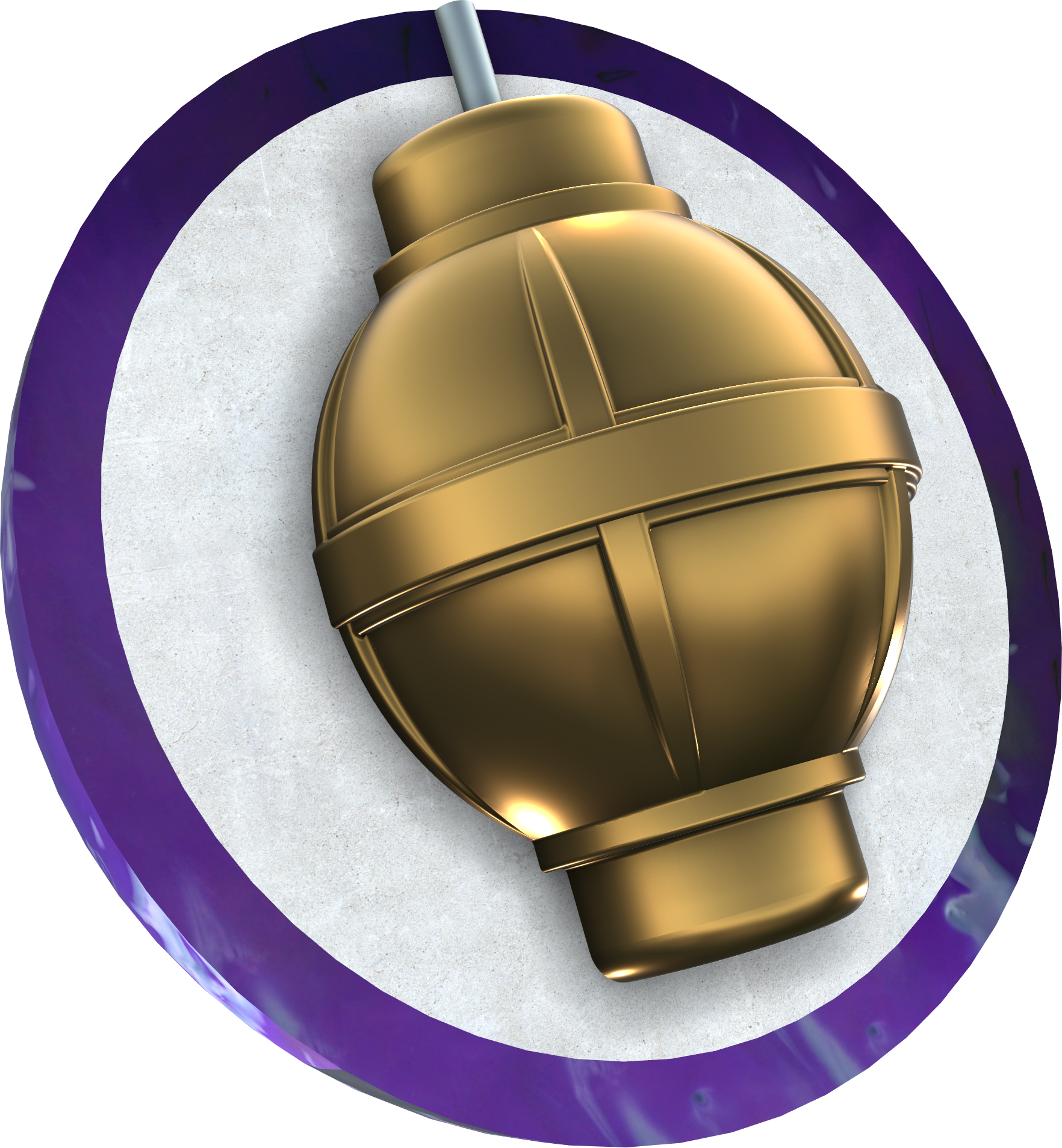
In contrast to symmetrical cores, asymmetrical cores have an uneven shape. This design can generate more aggressive hooking actions and complex roll patterns. The nuances of an asymmetrical core’s performance often require advanced knowledge and skill to leverage effectively, making these cores popular among pro bowlers.
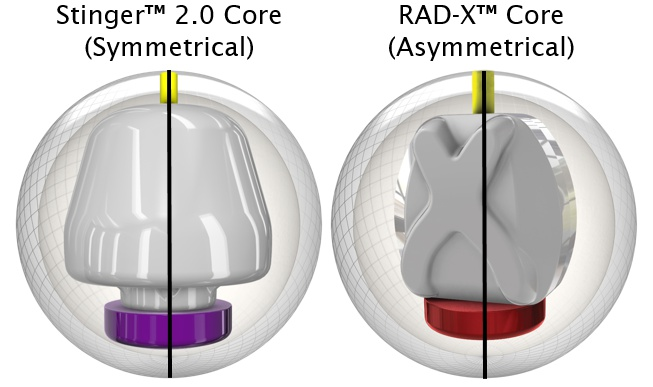
Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Core
Cheap vs Expensive Bowling Balls – The Best Option for Beginners?
The main difference between cheap and expensive bowling balls lies in the materials used and the complexity of the design.
Cheap Bowling Balls
Cheap bowling balls usually have a basic pancake core and a polyester coverstock.
The pancake core gives the ball a simple, predictable roll, while the polyester coverstock provides durability and straight movement on the lane. These balls are great for beginners and casual bowlers who are mainly bowling for fun or just learning the game basics.
Expensive Bowling Balls
Expensive bowling balls feature complex symmetrical or asymmetrical cores and reactive resin or particle (proactive) coverstocks.
The advanced core design enhances hook potentials, while high-end coverstocks offer better traction and control by interacting with lane oils. These sophisticated balls are preferred by pro bowlers and skilled amateurs for improved gameplay. The higher price reflects the advanced technology and high-quality materials used.

The Asymmetrical Core of a High-end Bowling Ball
Does the Inside of the Bowling Ball Matter?
Absolutely, the interior construction of a bowling ball significantly affects its performance on the lane.
The core design impacts balance, spin, and hook potential, while the filler material influences weight and distribution. Understanding how the ball interacts with the coverstock and lane conditions gives you an edge. Choose the right ball with the appropriate core and filler for a better game, whether you’re a novice or a pro.
Fun Facts About Bowling Balls
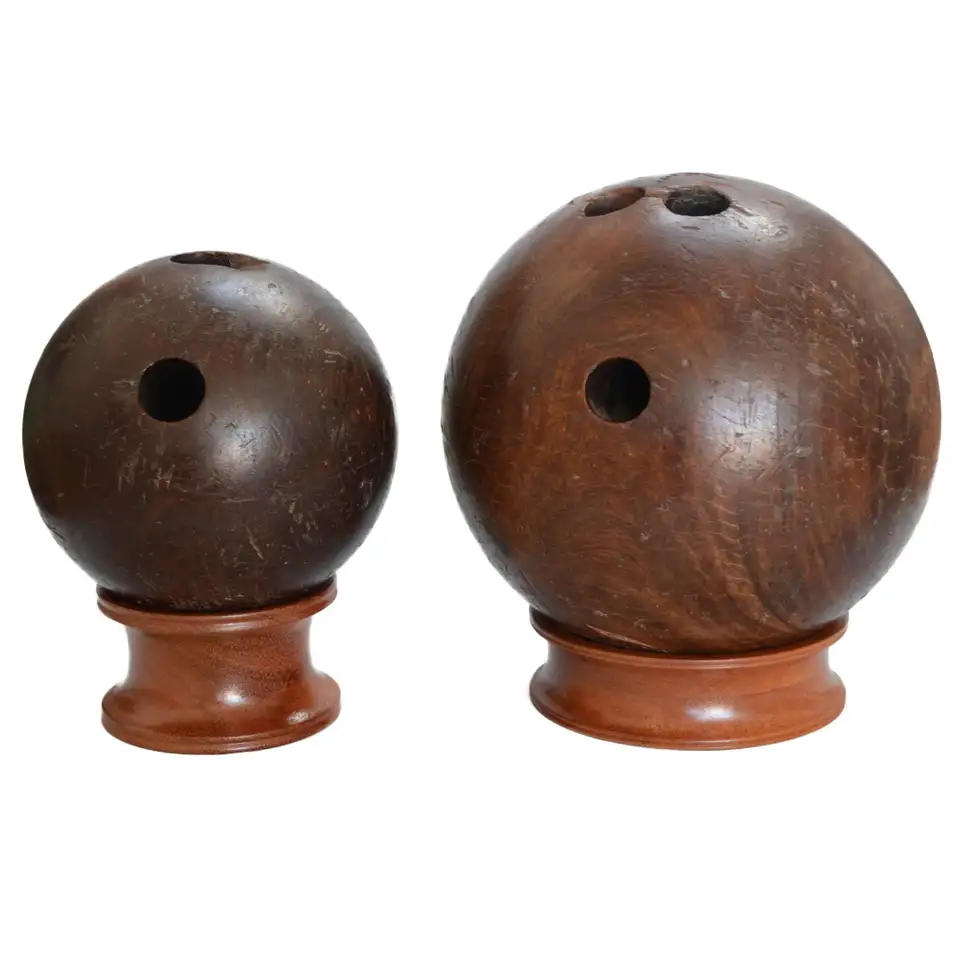
Bowling Balls made of… Wood?
That’s right! In fact, the very first bowling balls, used in ancient Egyptian times, were crafted from husk grains bound with a material like leather, and shaped into round balls.
Hardwood was cheaper, but it didn’t last as long. Additionally, cracked wooden balls had to be replaced when they split into pieces.

Do Bowling Balls Have Liquid Centers?
No, they don’t. I’ve had a few bowling balls crack, but they’ve never leaked. They were simply cracked.
While this myth has floated around for years, the fact is that all bowling balls, from the inexpensive to the high-end ones, have solid cores.
Hole-less Bowling Ball
Bowling balls start their lives hole-less. Custom drilling to match the bowler’s hand size only takes place once the ball is purchased. This allows for a perfect fit and a more comfortable game!
All Bowling Balls Are the Same Size
Despite their varying weights and different internal designs, all tenpin bowling balls have the same diameter: 8.5 inches (21.59 cm). This uniform size holds true for bowling balls used in competitions worldwide, providing a standardized challenge for all bowlers.

Conclusion
So now you know, that bowling balls aren’t hollow. Whether you’re a newbie or a pro, knowing how a bowling ball is built can seriously up your game. From the outer coverstock to the core design, every part plays a crucial role in performance. No matter the core shape, all cores are solid and affect weight and roll behavior. Just keep in mind, that you’re rolling a solid, carefully designed ball that’s got the momentum and power to scatter those pins for that super-satisfying strike!

Allow me to introduce myself – I’m Eric Wilkinson, a true bowling aficionado. The world of bowling culture has always fascinated me, and I’ve made the exciting decision to share my passion through writing. As I embark on this blogging adventure, my goal is to provide fellow enthusiasts with valuable insights, tips, and captivating stories. Through my blog, I hope to ignite a deeper appreciation for the sport and foster a sense of community among fellow bowlers. Join me on this thrilling journey as we explore the vibrant world of bowling together.
